Whatever content you publish on the Web and whatever website you run, you obviously want to be trusted by Google. If your content is unique and relevant if you don’t copy and paste the articles from someone else’s blogs, don’t spam, create something exclusive and uncommon, and optimize your content for SEO, then you will easily make steps to rising your website in Google search results and gaining better traffic.
There is a number of Google algorithms that prove your website content is relevant and then show it in the search results on a certain position (depending on the rankings). Usually, these algorithms are regularly updated, but not all of them are confirmed by Google.
What is a Google algorithm?
Initially, algorithms are considered to be a set of rules that a certain app should strictly follow for definite operations. Google was also made as a set of codes called algorithms. A regular Google algorithm is a set of commands created to send feedback including the search results relevant to the queries made by users. Google algorithms are dynamic and intelligent.
What’s the difference between confirmed and unconfirmed Google algorithms?
Actually, there is almost no difference between confirmed and unconfirmed algorithms by Google because both of them impact your page rankings depending on the quality of your content.
Most of the algorithm updates that affected many websites worldwide hadn’t been named or confirmed by Google. It’s very seldom for Googlers to officially confirm a lot of their algorithms; usually they make it a few times a year.
Each update announced by Google make some websites either gain or lose traffic depending on the relevance of their content. Some websites can be even penalized by Google algorithms, and this is what all website owners are afraid of.
In this post we’ve decided to review all of the latest confirmed Google algorithm updates made since the fall 2016. This was the period we started running our blog at WP Daddy, so let’s see what has been changed since then.
The Latest Updates by Google
1. Penguin 4.0 — September 23, 2016

The very first Penguin algorithm was issued in April 2012 (it was first unofficially named a WebSpam Update). The algorithm adjusted a list of spam factors like keyword density, and some more. Since then Penguin has been regularly updated.
A few years before 2016, there was nothing heard about Penguin, and finally on September 23, 2016 it came out as a 4.0 update. Since then this update has become a part of Google’s core algorithm.
The main change that affected the websites was that Penguin started refreshing in real time mode. Website penalties were either incurred or lifted every time a Google spider crawled a web-page or reindexed it.
– Penguin 4.0, Phase 1 — September 27, 2016
This update made Penguin a bit milder. Now instead of penalizing websites at once it made the bad links lose their value.
– Intrusive Interstitial Penalty — January 10, 2017
This update was meant to punish websites using obtrusive ads and popups to attract customers. These popups were not only disturbing for users but also damaged the mobile UX.
2. Unnamed Update — February 6, 2017
These updates are somehow connected to Google’s Panda algorithm update launched in January 2016 (the initial release of Panda was first announced in February 2011). The unnamed update of February 6, 2017 supposed some changes in relevancy of definite queries while Panda update of January, 2016 was meant to provide more visibility to websites with high quality content as well as lower the ranks of websites with content of worse quality. This update became the part of the core algorithm.
The unnamed update of 2017 also affected websites with spammy ads, broken interfaces or menus, and other peculiarities that damaged the UI and mobile UX. Low quality content and bad mobile responsiveness also became the reasons for this update to punish some websites.
3. Google Jobs — June 20, 2017
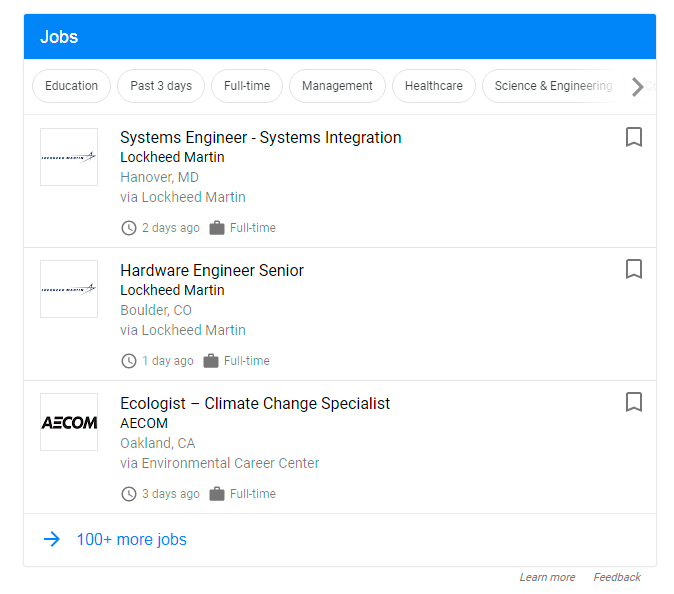
In June 2017 Google officially launched their own jobs portal, so now you can type “jobs” in the Google search field and see a box labeled ‘Jobs’ beneath the search bar. The search results show the information from most of the key job providers like Glassdoor, CareerBuilder, LinkedIn, and more.
4. Chrome Security Warnings (Forms) — October 17, 2017

In October 2017 the 62 version of Google Chrome browser was released. Since then all website visitors started to receive warnings when entering websites with http protocol instead of https. These websites has no SSL certificates activated so they’ve got unsecured forms.
This change wasn’t actually an algorithm update but it still has an impact on website traffic if a website isn’t able to prove it is secure.
5. Snippet Length Increase — November 30, 2017

The initial length of a meta description was 155 characters, but in November 2017 it was almost doubled and increased to 300 characters in length. Google snippets looked more comprehensive and rich. Though Google confirmed the new snippet handling but the details weren’t provided.
6. “Brackets” Core Update — March 8, 2018

This update started on March 4 and continued up to March 8, 2018. This was a broad core algorithm update which Google usually makes several times a year. This update was focused on content quality, so it influenced higher quality websites rising to the top and supporting their rich snippets as a result.
7. Zero-Result SERP Test — March 14, 2018
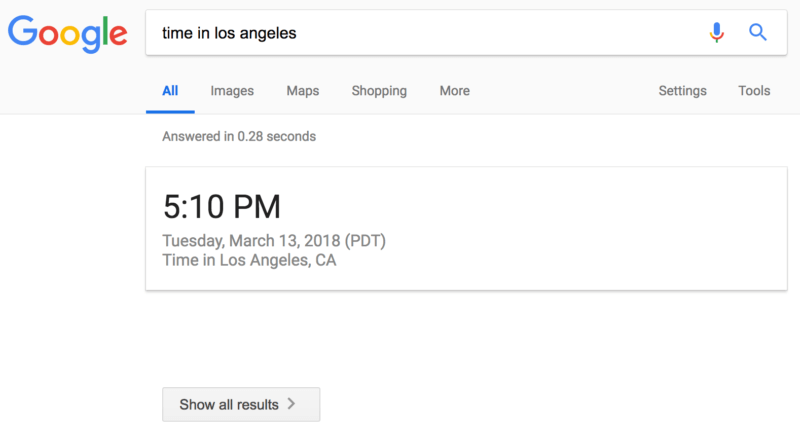
This update can be called a test one. For a certain period of time users were able to observe zero organic results as well as a ‘Show All Results’ button. In a week these updates were stopped to be shown. Probably this test was a sign that something would be changed in the closest future.
8. Mobile-First Index Roll-out — March 26, 2018

Previously Google used the desktop versions of displaying the web-page content to crawl, index and rank it. This could result in some problems for mobile users to properly perceive the content they find in Google SERPs.
Mobile-first indexing update was made to use the mobile versions of the websites for primary indexing and ranking. A webmaster was able to start seeing notifications in the Google Search Console.
9. Unnamed Core Update — April 17, 2018

This Google update was called upon to adjust rankings to make sure that users got the results that met their queries the best. The basis of this algorithm update was related to the content relevance.
10. Snippet Length Drop — May 13, 2018
In May 2018 the length of Google snippets was dropped again. Now meta description was again limited to 150 characters instead of the former 300 ones.
11. Video Carousels — June 14, 2018
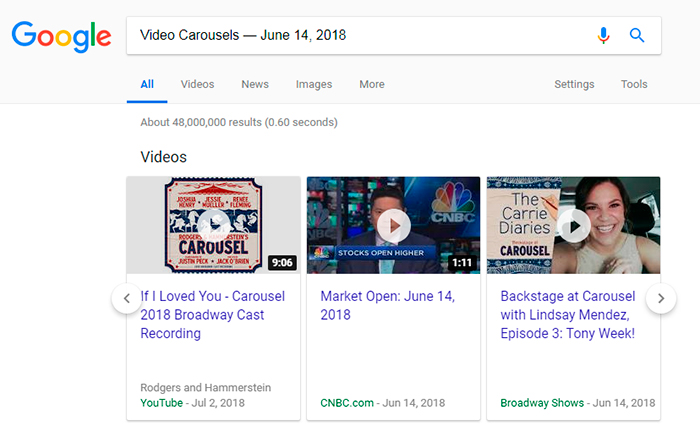
Videos were moved from organic-like results together with thumbnails into a video carousel in the desktop search engine result pages. Despite of the fact that video carousels were always mainly intended for mobile; they replaced the video thumbnails in desktop Google SERPS.
12. Mobile Speed Update — July 9, 2018

This update was made to consider a page speed to be a ranking factor for mobile search results. The update didn’t affect the websites with average speed, however, it caused problems for the slowest web-pages.
13. Chrome Security Warnings (Full Site) — July 24, 2018
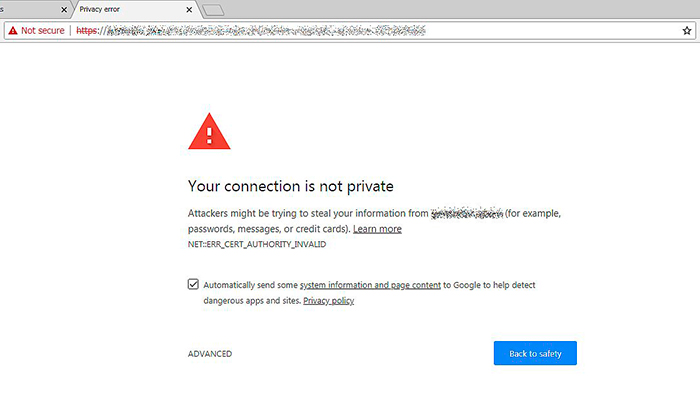
Another Chrome security warning update was announced in July, 2018. The 68 version of this browser started to mark all http websites as not secure ones. So it was a reason for many webmasters to buy SSL certificates and transform their http into https.
14. “Medic” Core Update — August 1, 2018

Google calls this update a broad and core one but some researches prove this is focused on medical websites which have been affected the most.
Google states you can do nothing to improve your website to meet the requirements of this update; all you can do is offering good user experience, quality content and useful information.
Final Thoughts
The updates are going to be continued, so we will stay tuned. We recommend you to also monitor these updates to make your website better for your users and your page ranking.





